Prime Factorization
Prime Number:
A number which is divisible by 1 and by itself is called prime number.
Prime Factorization:
If a given number say 24 is divided by 2 we start getting the factors has 24= 2$\times$2 $\times$2 $\times$ 3. Here 2 and 3 are prime factors. So 24 = 23 $\times$3.
Now let us learn to solve prime factorization with these below examples:
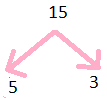
Prime Factors of 15
15 = 5$\times$3.
Step 1: Divide 15 by 3
Step 2: we get 5
so prime factors are illustrated below
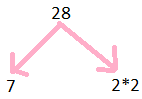
Prime Factors of 28
28 = 2$\times$2$\times$7.
Step 1: Divide 28 by 2
Step 2: we get 14
Step 3: further divide by 2
Step 4: we get 7
so prime factors are illustrated below
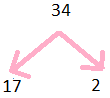
Prime Factors of 34
34 = 2$\times$ 17
Step 1: Divide 34 by 2
Step 2: we get 17
so prime factors are illustrated below
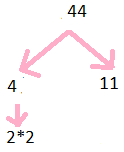
Prime Factorisation of 44
44 = 2$\times$2$\times$11
Step 1: Divide 44 by 2
Step 2: we get 22
Step 3: further divide by 2
Step 4: we get 11
so prime factors are illustrated below
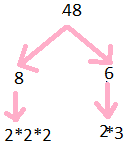
Prime Factorisation of 48
48 = 2$\times$2$\times$2$\times$2$\times$3
44 = 2$\times$2$\times$11
Step 1: Divide 48 by 2
Step 2: we get 24
Step 3: further divide by 2
Step 4: we get 12
Step 5: further divide by 2
Step 6: we get 6
Step 7: further divide by 2
Step 8: we get 3
so prime factors are illustrated below
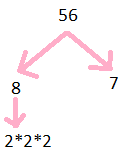
Prime Factorisation of 56
56= 2$\times$2$\times$2$\times$7
Step 1: Divide 56 by 2
Step 2: we get 28
Step 3: further divide by2
Step 4: we get 14
Step 5: further divide by 2
Step 6: we get 7
so prime factors are illustrated below
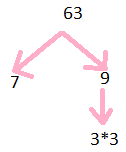
Prime Factorisation of 63
63= 3$\times$3$\times$9
Step 1: Divide 63 by 3
Step 2: we get 21
Step 3: further divide by 3
Step 4: we get 7
so prime factors are illustrated below
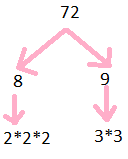
Prime Factorisation of 72
72= 2$\times$2$\times$2$\times$3$\times$3
Step 1: Divide 72 by 2
Step 2: we get 36
Step 3: further divide by 2
Step 4: we get 18
Step 5: further divide by 2
Step 6: we get 9
Step 7: divide it by 3
Step 8: we get 3
so prime factors are illustrated below
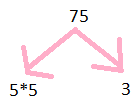
Prime factorisation of 75
75= 5$\times$5$\times$3
Step 1: Divide 75 by 5
Step 2: we get 15
Step 3: further divide by 5
Step 4: we get 3
Step 5: further divide by 3
Step 6: we get 1
so prime factors are illustrated below
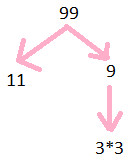
Prime Factorisation of 99
99 = 3$\times$3$\times$ 11
Step 1: Divide 99 by 3
Step 2: we get 33
Step 3: further divide by3
Step 4: we get 11
Step 5: further divide by 11
Step 6: we get 1
so prime factors are illustrated below
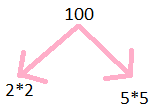
Prime factorisation of 100
100 = 2$\times$2$\times$5$\times$5
Step 1: Divide 100 by 5
Step 2: we get 20
Step 3: further divide by 5
Step 4: we get 4
Step 5: further divide by 2
Step 6: we get 2
Step 7: further divide by 2
Step 8: we get 1.
so prime factors are illustrated below
Average Acceleration Calculator
Average acceleration is the object's change in speed for a specific given time period. ...
When an object falls into the ground due to planet's own gravitational force is known a...
In Mathematics, the permutation can be explained as the arrangement of objects in a particular order. It is an ordered...
A rectangle can be explained as a 4-sided quadrilateral which contains equal opposite sides. In a rectangle
A three sided polygon which has three vertices and three angles is called a triangle. Equilateral triangle...





